The direction of light changes upon changing mediums(e.g. from air to water, or glass).
This is in part due to the speed of light being dependent on the properties of the medium; light is absorbed and reemitted for different amounts of time depending on material properties, and amounts to a significant difference in overall speed per medium.
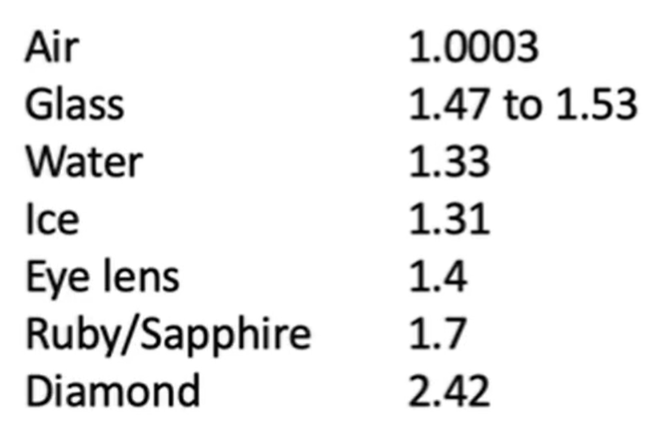
The ratio of the speed of light in a vacuum to that in a medium is the index of refraction. This ratio is always greater than one, as the the speed of light is faster in a vacuum than in any medium. For example:
This change in speed causes the change in direction, as per Christian Huygen’s theory. The behaviour of light as it goes from one medium to another is known as Snell’s law, shown in the equation. The angle is measured relative to the normal of the surface, regardless of the direction in which the light goes. The ray ‘bends’ towards the normal in the medium with a higher index of refraction.
If the angle is too shallow, it gets reflected back into the medium.